Your voice is more than just a means of communication—it’s an essential part of your identity, self-expression, and professional life. When voice disorders arise, they can significantly impact daily activities and overall quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the early signs of voice disorders, understand their various causes, and examine how modern diagnostic tools are revolutionizing the field of voice disorder detection and treatment.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Voice Production
Before delving into voice disorders, it’s crucial to understand how a healthy voice functions. Your voice is produced through a complex interaction of multiple body systems. The larynx, commonly known as the voice box, houses the vocal cords—two bands of elastic muscle tissue that vibrate to produce sound when air passes between them. These vibrations, combined with resonance in the throat, nose, and mouth, create your unique voice with its characteristic pitch, loudness, and tone.
A normal, healthy voice should:
- Maintain consistent quality throughout the day
- Allow for variation in pitch and volume without strain
- Enable clear articulation of words
- Function without discomfort or fatigue
- Support both speaking and singing (within one’s natural range)
Types of Voice Disorders
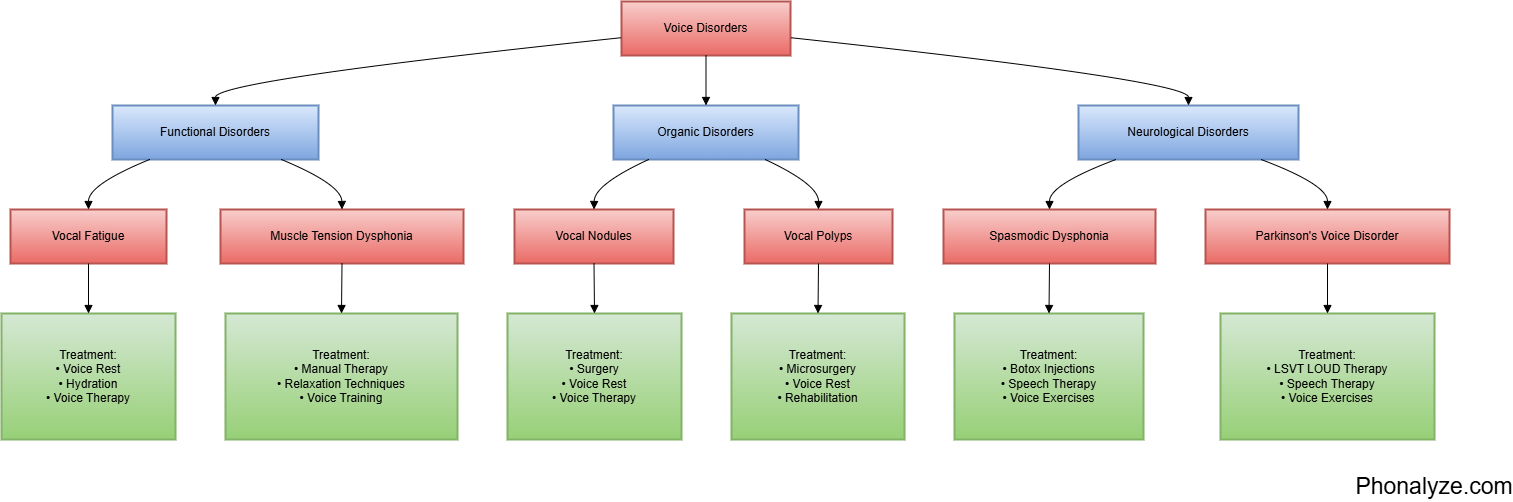
Voice disorders fall into three main categories, each with distinct characteristics and treatment approaches:
Functional Voice Disorders
Functional disorders arise from improper voice use or muscle tension patterns. These conditions often develop gradually and may be related to behavioral patterns or environmental factors. Common examples include:
Vocal Fatigue: Perhaps the most prevalent functional disorder, vocal fatigue occurs when voice quality deteriorates with prolonged use. Teachers, call center workers, and public speakers frequently experience this condition. The voice typically feels tired, strained, and may become progressively hoarse throughout the day.
Muscle Tension Dysphonia: This condition develops when excessive tension in the muscles surrounding the larynx interferes with normal voice production. Individuals might experience a feeling of “pushing” or straining to produce voice, often accompanied by neck tension and discomfort.
Organic Voice Disorders
Organic disorders involve physical changes to the vocal cords or surrounding structures. These can be either temporary or permanent:
Vocal Nodules: Similar to calluses on the vocal cords, nodules typically develop from prolonged voice misuse. They often appear in pairs on opposite sides of the vocal cords and can significantly affect voice quality.
Laryngitis: This inflammation of the vocal cords can be acute (short-term) or chronic. Viral infections most commonly cause acute laryngitis, while chronic cases might result from ongoing irritation or reflux disease.
Polyps: These soft, fluid-filled lesions can develop on one or both vocal cords, often resulting from vocal trauma or prolonged irritation. Smokers and professional voice users are particularly susceptible.
Neurological Voice Disorders
These disorders stem from problems with nerve function affecting the larynx:
Spasmodic Dysphonia: This neurological condition causes involuntary spasms of the vocal cords, resulting in a strained, broken, or tremulous voice quality. The condition can significantly impact communication and often requires specialized treatment approaches.
Parkinson’s-Related Voice Changes: Individuals with Parkinson’s disease frequently experience voice changes, including reduced volume, monotone speech, and difficulty initiating speech.
Early Warning Signs: When to Pay Attention
Recognizing early signs of voice disorders is crucial for timely intervention and successful treatment. Here are the key symptoms to watch for:
Immediate Red Flags
Voice Quality Changes:
- Persistent hoarseness lasting more than two weeks
- Breathiness or weakness in voice production
- Unexpected changes in pitch range
- Voice breaks or crack during speech
Physical Sensations:
- Throat pain or discomfort while speaking
- Feeling of tightness or tension in the throat
- Chronic throat clearing or coughing
- Sensation of a lump in the throat
Progressive Symptoms
Some voice disorders develop gradually, with symptoms becoming more noticeable over time:
- Increased effort needed to produce voice
- Progressive loss of vocal range
- Voice fatigue occurring earlier in the day
- Difficulty projecting voice in noisy environments
- Morning voice taking longer to “warm up”
Modern Diagnostic Tools: The Technology Revolution
The field of voice disorder diagnosis has been transformed by technological advances, offering more precise and objective assessment methods than ever before:
Traditional Diagnostic Methods
Laryngoscopy remains a foundational tool in voice disorder diagnosis. This procedure allows direct visualization of the vocal cords and surrounding structures. Modern versions include:
Flexible Laryngoscopy: A thin, flexible fiber-optic tube with a camera is passed through the nose to observe the larynx during natural speech and swallowing.
Videostroboscopy: This specialized technique uses strobe lighting to create a slow-motion effect of vocal cord vibration, enabling detailed analysis of vibratory patterns.
Advanced Technological Solutions
Acoustic Analysis Software:
Modern acoustic analysis tools can measure and quantify various aspects of voice production:
- Fundamental frequency (pitch)
- Intensity (loudness)
- Jitter and shimmer (voice stability measures)
- Harmonic-to-noise ratio
- Voice range profiles
These measurements provide objective data about voice function and can track treatment progress over time.
Artificial Intelligence in Voice Analysis:
AI-powered systems are revolutionizing voice disorder diagnosis through:
- Pattern recognition in voice samples
- Early detection of subtle voice changes
- Predictive analysis for disorder progression
- Automated screening tools for large populations
High-Speed Digital Imaging:
This technology captures thousands of frames per second of vocal cord movement, providing unprecedented detail about vibratory patterns and enabling detection of subtle abnormalities.
The Role of Speech-Language Pathologists
Speech-language pathologists (SLPs) play a crucial role in voice disorder diagnosis and treatment. Their approach typically involves:
Comprehensive Assessment
SLPs conduct detailed evaluations including:
- Case history review
- Perceptual voice analysis
- Acoustic measurements
- Quality of life impact assessment
- Functional voice use evaluation
Treatment Planning
Based on diagnostic findings, SLPs develop individualized treatment plans that may include:
- Voice therapy exercises
- Behavioral modification techniques
- Respiratory support training
- Vocal hygiene education
Preventive Measures and Voice Care
Maintaining vocal health is crucial for preventing voice disorders. Here are essential preventive strategies:
Vocal Hygiene Practices
Hydration:
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day
- Maintain proper humidity in living and working spaces
- Avoid excessive caffeine and alcohol
Voice Use:
- Practice appropriate vocal warm-ups before heavy voice use
- Take regular voice breaks during periods of extensive speaking
- Avoid shouting or speaking over loud noise
Environmental Factors:
- Minimize exposure to irritants like smoke and dust
- Use appropriate amplification when speaking to large groups
- Maintain good posture and breathing habits
Conclusion
Voice disorders represent a complex group of conditions that can significantly impact daily life and professional function. Thanks to advances in diagnostic technology and treatment approaches, these conditions can be identified earlier and managed more effectively than ever before. If you experience persistent voice changes or discomfort, don’t wait to seek professional evaluation—early intervention often leads to better outcomes.
Remember that your voice is a crucial tool for communication and self-expression. Understanding the signs of voice disorders and knowing when to seek help can make a significant difference in maintaining vocal health and preventing long-term problems. Whether you’re a professional voice user or someone concerned about voice changes, modern diagnostic tools and treatment approaches offer hope and solutions for maintaining optimal vocal function.
For Read About How AI Help Laryngologists
